Controlling blood glucose levels
Detecting diabetes
The simplest way to detect diabetes is to look for glucose in the urine. A glucose test stick changes colour to indicate the level of glucose.
Diabetics regularly monitor their blood glucose level by using a digital monitor. A drop of blood is placed on a test strip and the monitor displays the blood glucose concentration.
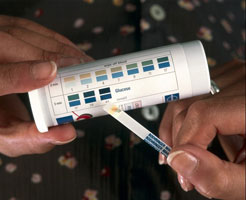
Simple test sticks can indicate the presence of glucose in the urine.
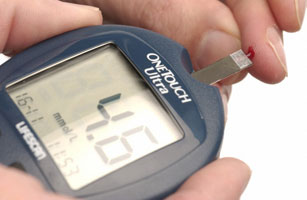
Self-monitoring of blood glucose levels is an important aspect of living with diabetes.
Images courtesy of: Wellcome Images
Glucose tolerance test
To confirm diabetes, a person will normally take a glucose tolerance test in a hospital.
Patients do not eat for 12 hours before the test. This gets their blood glucose to its lowest level. They are then given a drink containing 75g of glucose and their blood glucose level is monitored over the next two hours.
Diabetics will rapidly become hyperglycaemic. Their blood glucose level rises and remains above normal.
Healthy individuals will release insulin to store the excess glucose. Their blood glucose level rises but then returns to normal.
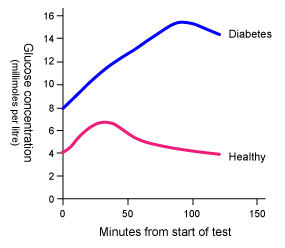
Blood glucose in the diabetic rises and stays above normal.
The healthy person regulates their glucose back to normal.
Control of blood glucose levels
Every cell in the body needs a supply of glucose to maintain respiration and generate energy for all of its processes. Levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood are closely controlled by two hormones ; insulin and glucagon .
Use the animation to see how the body responds to high and low blood sugar levels:
Question 2
Drag the responses into the correct columns
| Blood sugar too high | Blood sugar too low |
|---|---|